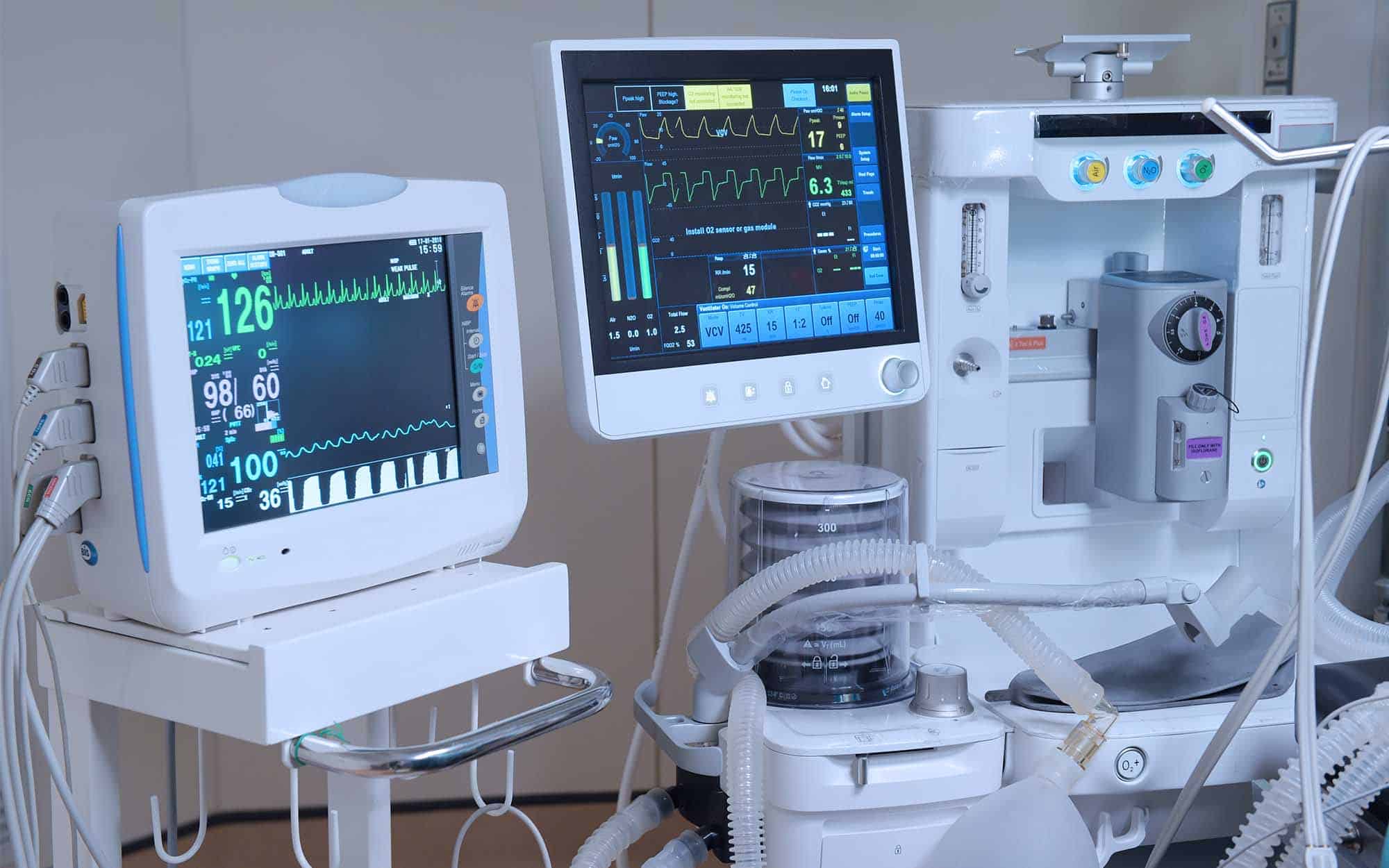
1. Diagnostic Devices
- Ultrasound Machines: Use sound waves to create images of internal organs and tissues.
- X-ray Machines: Utilize X-rays to take images of the inside of the body, commonly used to detect fractures or lung conditions.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): Combines X-ray images with computer processing to create cross-sectional images of bones and soft tissues.
- MRI Machines (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Use strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of soft tissues.
- ECG/EKG (Electrocardiogram): Records the electrical activity of the heart, helping to diagnose heart conditions.
- EEG (Electroencephalogram): Measures electrical activity in the brain, used for diagnosing neurological conditions like epilepsy.
- Blood Glucose Meters: Devices used by diabetic patients to monitor blood sugar levels.
- Pulse Oximeter: Measures the oxygen saturation level in the blood, commonly used to monitor respiratory conditions.
2. Therapeutic Devices
- Ventilators: Machines that assist or control breathing in patients who are unable to breathe on their own.
- Infusion Pumps: Devices used to administer fluids, medications, or nutrients directly into the bloodstream.
- Dialysis Machines: Used to filter waste from the blood in patients with kidney failure.
- Radiation Therapy Machines: Used for the treatment of cancer by delivering targeted doses of radiation to tumors.
- Laser Therapy Devices: Use light to treat various conditions, including skin disorders and eye conditions like cataracts.
- Electrotherapy Equipment: Used in physical therapy to help stimulate muscles, reduce pain, or improve circulation.
- Pacemakers: Implanted devices that regulate the heartbeat in patients with arrhythmias.
- Defibrillators (AED): Devices that deliver an electric shock to the heart to restore a normal rhythm in case of cardiac arrest.
3. Monitoring Devices
- Blood Pressure Monitors: Devices used to measure the force of blood against artery walls, important for monitoring hypertension.
- Heart Rate Monitors: Track the beats per minute (BPM) of the heart, often used by patients with cardiovascular concerns.
- Fetal Monitors: Used during labor to monitor the baby’s heartbeat and the mother’s contractions.
- Temperature Sensors: Measure body temperature to help diagnose infections or illnesses.
- Electroencephalograph (EEG) Monitors: Continuously track brain activity in patients with neurological conditions.
- Capnographs: Measure the concentration of carbon dioxide in exhaled air, used for monitoring ventilation.
4. Assistive Devices
- Wheelchairs: Manual or motorized chairs for patients with mobility issues.
- Crutches and Walkers: Used to support patients during walking, often after surgery or injury.
- Prosthetics: Artificial limbs or body parts used to replace missing body parts.
- Hearing Aids: Devices that amplify sound to help individuals with hearing loss.
- Cochlear Implants: Surgically implanted devices to provide a sense of sound to people with severe hearing loss.
- Orthotic Devices: Supports or braces for joints or bones to aid in movement or correct deformities (e.g., back braces, knee supports).
5. Surgical Instruments
- Scalpels: Surgical knives used for making incisions during surgery.
- Surgical Scissors: Used for cutting tissues or sutures during procedures.
- Forceps: Tweezer-like instruments used for grasping or holding tissues during surgery.
- Needles and Syringes: Used for injecting medications or drawing blood.
- Surgical Drills: Used in orthopedics to create holes in bones, typically for screws or pins.
- Electrosurgical Units: Use electrical currents for cutting tissue or coagulating blood vessels during surgery.
6. Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy Devices
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) Units: Use low-voltage electrical currents to relieve pain and muscle spasms.
- Physical Therapy Equipment: Includes devices such as resistance bands, stationary bikes, and machines for strengthening muscles and improving mobility.
- CPM (Continuous Passive Motion) Machines: Used in post-surgical recovery to keep joints moving.
- Orthopedic Braces and Supports: Provide support to injured or weakened joints, ligaments, or bones.
- Gait Trainers: Devices designed to help individuals relearn how to walk after injury or stroke.
7. In-Vitro Diagnostic Devices
- Pregnancy Test Kits: Home diagnostic tests to detect pregnancy hormones in urine.
- Urine Test Strips: Used to detect specific substances in urine, such as glucose, protein, or pH levels.
- Blood Gas Analyzers: Devices used to measure the levels of gases in the blood (such as oxygen and carbon dioxide).
- HIV/STD Test Kits: Home or laboratory tests to detect sexually transmitted infections.
8. Patient Care Devices
- Hospital Beds: Adjustable beds designed to meet the needs of patients in a hospital setting.
- Patient Lifts: Devices used to lift and transfer patients from one place to another, particularly for those with limited mobility.
- Suction Devices: Used to remove fluids (e.g., mucus or blood) from a patient’s airway or wounds.
- Nebulizers: Devices that turn liquid medicine into a mist to be inhaled, often used for treating asthma or COPD.
9. Dental Devices
- Dental X-ray Machines: Used for capturing images of teeth and jawbones.
- Dental Implants: Artificial tooth roots placed into the jaw to support artificial teeth.
- Braces and Aligners: Devices used to straighten teeth and correct bite problems.
- Dentures: Removable replacements for missing teeth.
- Whitening Devices: Tools and treatments used to lighten the color of teeth.
10. Emergency and Critical Care Devices
- Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs): Portable devices used to restart the heart in case of cardiac arrest.
- CPR Masks and Equipment: Used to assist in performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) in emergencies.
- Trauma and First Aid Kits: Contain tools and supplies for managing emergency situations, such as bleeding or fractures.
- Emergency Ventilators: Portable devices used to assist or control breathing during emergencies.
11. Disinfection and Sterilization Devices
- Autoclaves: Use high-pressure steam to sterilize surgical instruments and other medical equipment.
- UV Sterilizers: Use ultraviolet light to kill bacteria and viruses on surfaces or in air.
- Disinfectant Wipes and Sprays: Used for cleaning and disinfecting surfaces in medical environments.
12. Miscellaneous
- Sterile Dressings and Bandages: Used for covering and protecting wounds.
- Temperature Control Devices: Such as incubators for newborns or warming devices for patients under anesthesia.
- Blood Collection Tubes: Used for drawing blood for laboratory tests.
These devices are essential for diagnosing, treating, and managing health conditions across various stages of care, from routine check-ups to intensive treatments in hospitals and clinics.